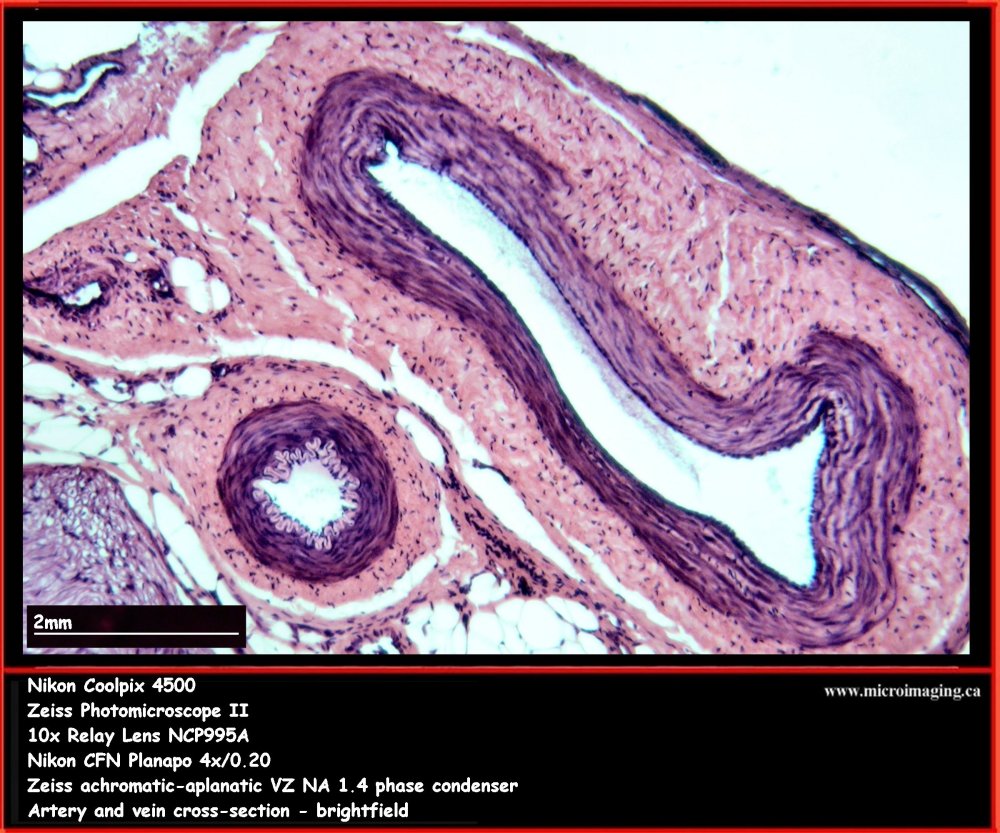
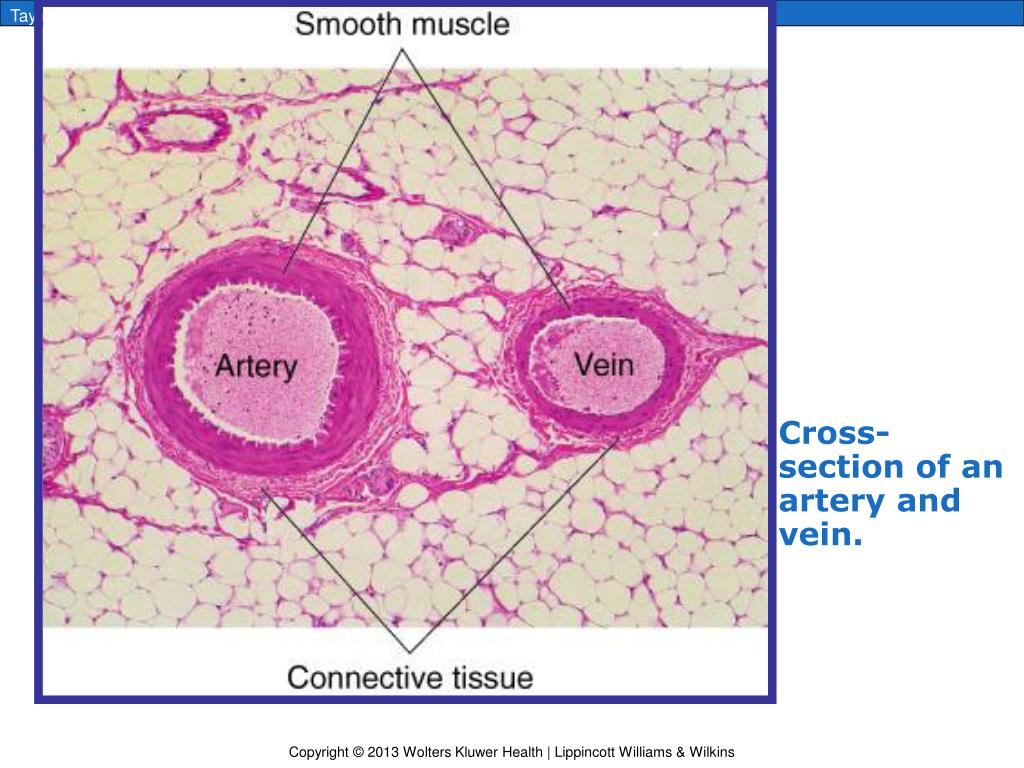
Artery & Vein, cross section
In all studied vein diameters, the blood flow changed accordingly: V ˙ = V × A, where, V ˙, V, and A are flow, velocity, and vein cross-sectional area, respectively. Effect of velocities The vein diameter assumed constant at 1.5 cm. 31,32 The stretch-recoil process shifts the blood flow in the center of the vein and consequently increases.
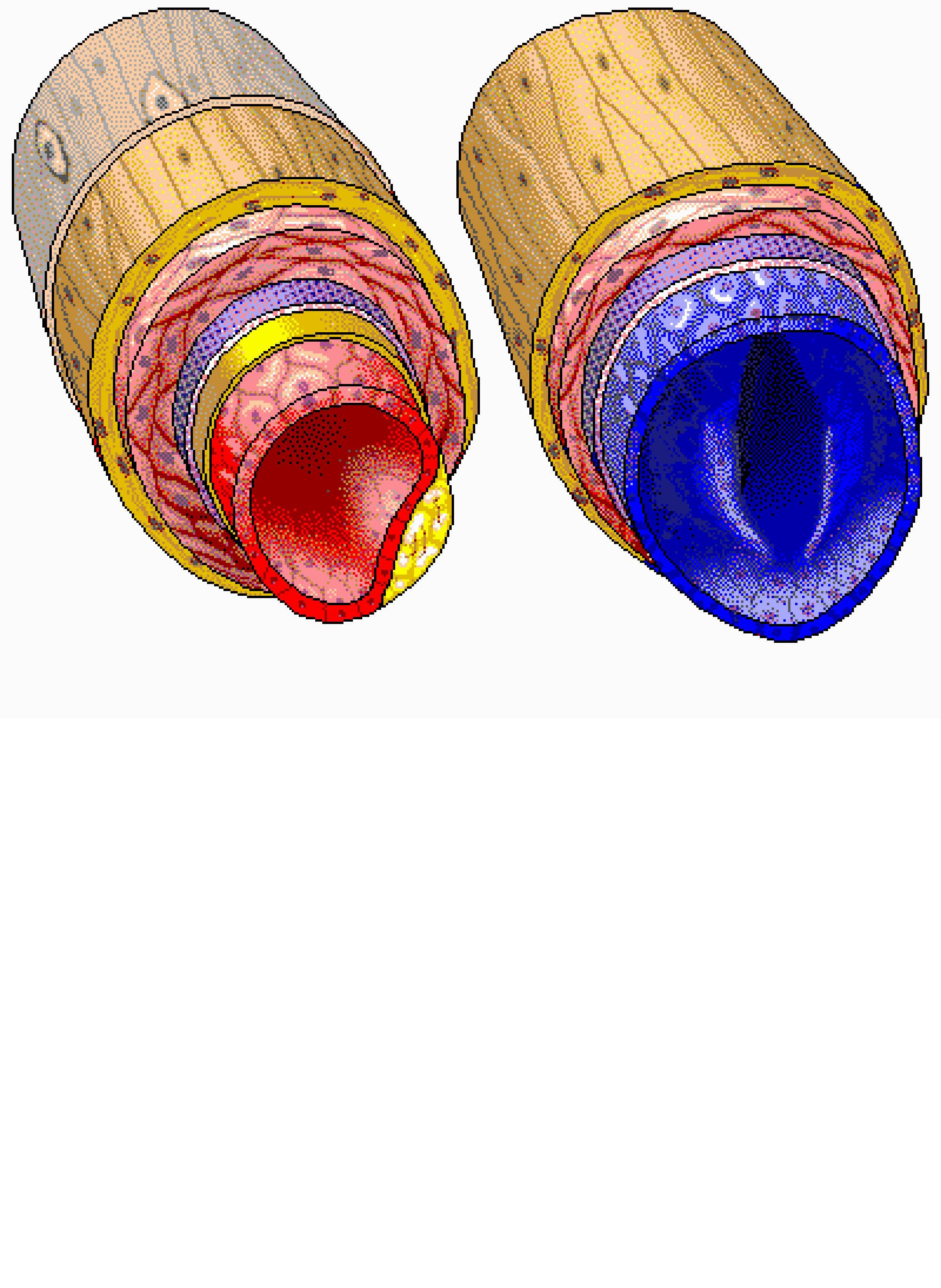
Arteries vs Veins Structure, Function & Blood Flow
The azygos venous system is located on either side of the vertebral column and drains the viscera within the mediastinum, as well as the back and thoracoabdominal walls. This system consists of the azygos vein and its two main tributaries: the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein.

LM of a crosssection through an artery and vein Stock Image P206/0116 Science Photo Library
Find an appropriate vein by scanning the arm in the transverse orientation, which provides a cross-sectional view of the anatomy and allows simultaneous visualization of veins, arteries, and other.

Vein and Artery anatomy. comparison and difference. longitudinal and cross section human blood
PURPOSE: To retrospectively establish normal values for pulmonary vein diameter, cross-sectional area, and shape depicted at computed tomography (CT). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Institutional review board waived patient consent requirement and approved the study. Thin-section contrast material-enhanced spiral chest CT scans in 104 patients, 68 women and 36 men (age range, 19-86 years; mean, 49.

Similarities and Differences Between Arteries and Veins Facty Health
Figure 40.10.1 40.10. 1: Blood vessel layers: Arteries and veins consist of three layers: an outer tunica externa, a middle tunica media, and an inner tunica intima. Capillaries consist of a single layer of epithelial cells, the endothelium tunic (tunica intima). Veins and arteries both have two further tunics that surround the endothelium: the.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-structure-of-the-vein-wall-87395965-58963cc63df78caebc05eee0.jpg)
Superior and Inferior Venae Cavae
1/7 Synonyms: Dorsal thalamus, Thalamencephalon , show more. Cross-sections are two-dimensional, axial views of gross anatomical structures seen in transverse planes. They are obtained by taking imaginary slices perpendicular to the main axis of organs, vessels, nerves, bones, soft tissue, or even the entire human body.
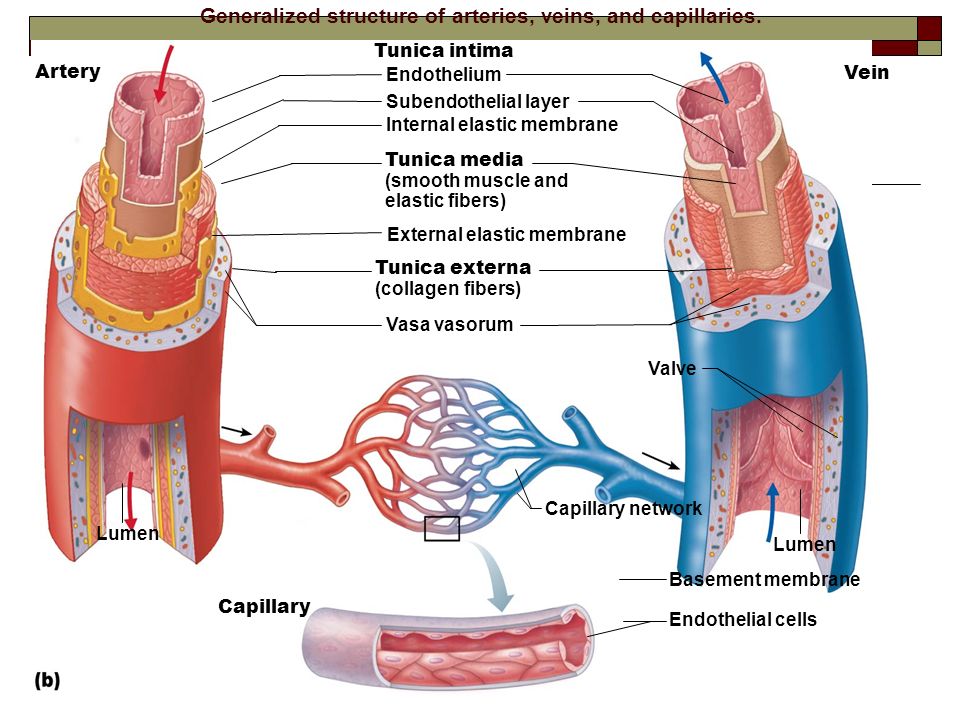
Blood Vessels Alisa Houghton
Wings of Matsucoccus pini males were studied. Using light and scanning electron microscopes, both sides of the wing membrane, dorsal and ventral, were examined. The presence of only one vein in the common stem was confirmed by the cross-section, namely the radius. The elements regarded as subcostal and medial veins were not confirmed as veins. On the dorsal side of the wings, a cluster of.

Anatomy Of Vein Longitudinal And Cross Section Stock Illustration Download Image Now Anatomy
Together, their thicker walls and smaller diameters give arterial lumens a more rounded appearance in cross section than the lumens of veins. Figure 20.3 Structure of Blood Vessels (a) Arteries and (b) veins share the same general features, but the walls of arteries are much thicker because of the higher pressure of the blood that flows through.

Micrograph illustrating a cross section of a medium size muscular artery, its vein
Blood vessel histology Author: Lorenzo Crumbie MBBS, BSc • Reviewer: Dimitrios Mytilinaios MD, PhD Last reviewed: October 30, 2023 Reading time: 17 minutes It would be impossible to get blood to the predestined locations without the vascular pathways. Blood vessels form the extensive networks by which blood leaves the heart to supply tissue. . Additionally, other blood vessels return from.

Blood Vessel Structure and Function Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Arteries and veins transport blood in two distinct circuits: the systemic circuit and the pulmonary circuit. Systemic arteries provide blood rich in oxygen to the body's tissues. The blood returned to the heart through systemic veins has less oxygen, since much of the oxygen carried by the arteries has been delivered to the cells.
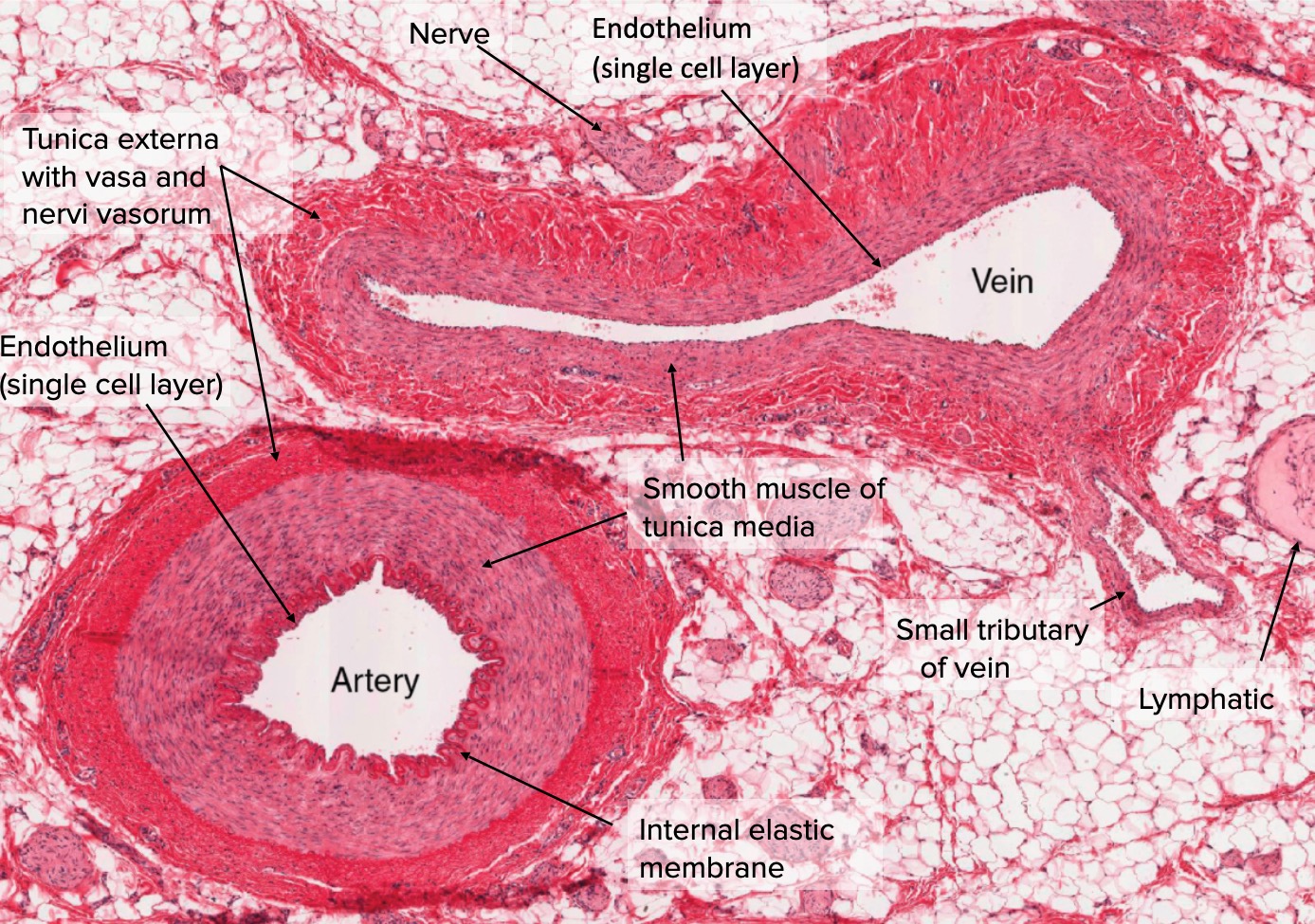
Pulmonary Artery Histology
The short-axis cross-sectional areas of the subclavian vein at the mid-clavicular line, the subclavian vein in the supraclavicular fossa, and the internal jugular vein at the level of the thyroid cartilage were calculated. Results

What are Blood Vessels? Types, Structure, & Functions hubpages
The presence of the costal vein was not observed on the cross-section during the present study. Our results are consistent with those produced for Orthezia urticae by Franielczyk-Pietyra et al. . The costal vein has not been recognized in wings of scale insects so far, e.g., [16,27,29,30].

Artery and Vein Cross Section Diagram Quizlet
Together, their thicker walls and smaller diameters give arterial lumens a more rounded appearance in cross section than the lumens of veins.. Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\): Varicose Veins. Varicose veins are commonly found in the superficial veins of the lower limbs. Defective valves cause localized pooling of blood in the veins that can lead to.
PPT Chapter 14 Blood Vessels and Blood Circulation PowerPoint Presentation ID5387380
The right hepatic vein is a single dominant vein in ~70% (range 60-78%) of individuals. There may be an early bifurcation, early trifurcation or even multiple right hepatic veins entering the IVC. Hence this may make it difficult to accurately deduce segmental anatomy of the liver. The commonest anatomical variant of the hepatic veins is an.

artery/vein cross section practical Diagram Quizlet
Veins are composed of xylem and phloem cells embedded in parenchyma, sometimes sclerenchyma, and surrounded by bundle sheath cells. The vein xylem transports water from the petiole throughout the lamina mesophyll, and the phloem transports sugars out of the leaf to the rest of the plant.

20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels Douglas College Human Anatomy and Physiology I
Assessment of the SSV Concluding the scan Vulval varicosities and pelvic incompetence B-mode appearance of varicose veins and perforators Investigation of recurrent varicose veins Possible causes of GSV recurrences Possible causes of SSV recurrences Assessment of patients with skin changes and venous ulceration Endovenous ablation of varicose veins